前言
本文的主要观点、代码片段、图片均源自《Test Double – xUnit Test Patterns》书的_Test Double_章节
很多时候,在执行单元测试时,待测对象依赖于其他模块,我们经常听到的有 Mock、Stub、Fake、Spy之类的词。 xUnit Test Patterns一书中对此进行了统称Test Double,并清晰的说明了各个术语的区别与应用场景。 下面主要从以下几个方面进行阐述:
- Four-Phase Test
- 理解Test Double
- Test Double的分类
- 实现方式
- 对比总结
一、Four-Phase Test
在开始步入正题 Test Double 之前,我们先大致看一下测试的 Four Phrase,以便我们可以on same page,不至于因为术语不同产生歧义。
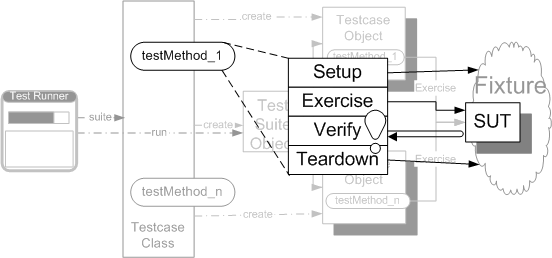
- 第一阶段,可以理解为做
GIVEN,做一些准备工作,其中可以包括创建test fixture以及设置 expectation。 - 第二阶段,可以理解为
WHEN,即和 SUT 进行交互。 - 第三阶段,可以理解为
TEHN,判断是否获取到了期望的输出或者行为。 - 第四阶段,做一些善后和清理操作,将系统还原成初始的样子。
二、理解Test Double
有时候,测试被测系统(System under test, SUT)非常困难,因为它依赖于其他组件,而这些组件在测试环境中无法使用。 这可能是因为这些组件不可用,亦或者是执行它们会产生副作用。在其他情况下,我们的测试策略要求我们对SUT的内部行为有更多的控制权或可见性。
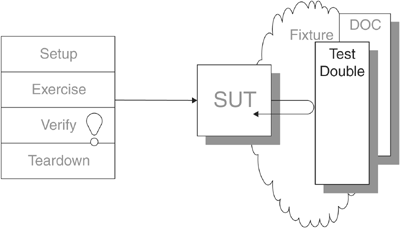
在编写测试时候,我们不能(或者不选择)使用一个真正的依赖组件( Depended-On Component,DOC),我们会用 Test Double 代替它。Test Double 不用有像真正的 DOC 一样的行为,只需要提供和真实的 API 相同的 API即可,这样SUT可以认为该 Test Double 就是真正的 API。
1. WHAT
在计算机编程和计算机科学中,程序员和开发人员使用称为自动化单元测试的技术来提高软件的质量。 通常情况下,最终版本软件由一组复杂的 对象或过程相互作用组成以创建最终结果。 在自动化单元测试中,可能有必要使用外观和行为与其发布相对应的对象或过程,但实际上用的却是简化 版本的对象和过程,以降低复杂性并促进测试。 Test Double是这些对象或过程的通用术语。
一句话介绍的话,Test Double是一个通用术语,用于在任何情况下,为了测试目的而替换生产对象。
2. WHY
- 减少对被测对象的依赖,使得测试更加单一
- 让测试案例执行的时间更短,运行更加稳定
- 对SUT(待测系统)内部的输入输出进行验证,让测试更加彻底深入
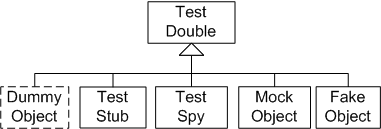
三、Test Double的分类
Test Double可以进一步细化为以下5种:
- Test Stub,桩,在测试中为每个调用提供一个封装好的响应,通常不会对测试之外的请求进行响应,只用于测试。
- Test Spy,是一种记录一些关于它们如何被调用的信息的桩。这种形式的桩可能是记录它发出去了多少个消息的一个电子邮件服务。
- Mock Object,模拟对象,是一种在编程时就设定了它预期要接收到调用。如果收到了为预期的调用,它会抛出异常,并且还会在 验证时被检查是否收到了它们所预期的所有调用。
- Fake Object,假对象,可以真正使用的实现,通常利用一些捷径,不适合在生产环境中使用,比如内存数据库(InMemoryTestDatabase)。
- Dummy Object,哑对象,是指那些被传递但不被真正使用的对象。通常用于添充参数列表。
1. Stub
Test Stub是指一个完全代替待测系统依赖组件的对象,这个对象按照我们设计的输出与待测系统进行交互。这个桩既不会与 测试用例(代码)交互,也不会在待测系统内部进行验证。
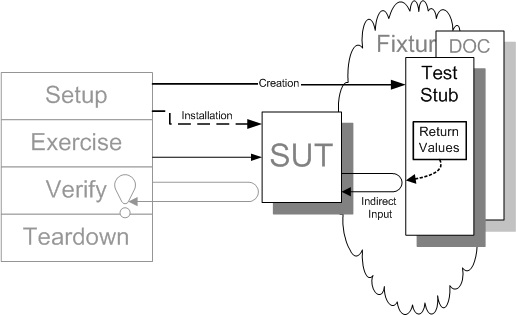
1.1 特点
- 完全代替待测系统依赖组件的对象
- 不会对 SUT 内部的输入进行验证
1.2 场景
- 依赖组件无法使用,影响测试结果
- 依赖组件运行太慢,影响测试速度
- 成为Responder响应者,当需要给待测系统注入特定数据,从而对待测系统产生影响
- 成为Saboteur破坏者,当需要给待测系统注入无效数据,从而对待测系统产生异常影响,观察待测系统如何处理错误情况
1.3 示例
- 初始测试 - 依赖组件无法使用 下面的代码只是测试了基本功能–格式化含有时间的 HTML 字符串,但是它依赖于真正的系统时钟。所以测试不会通过。
public void testDisplayCurrentTime_AtMidnight() {
// fixture setup
TimeDisplay sut = new TimeDisplay();
// exercise sut
String result = sut.getCurrentTimeAsHtmlFragment();
// verify direct output
String expectedTimeString = "<span class=\"tinyBoldText\">Midnight</span>";
assertEquals( expectedTimeString, result);
}
- 使用真正的系统时钟之后的测试 下面的代码引入了当前系统的时钟,但是又带来了两个问题:其一,有些测试条件永远不会执行(比如测试Midnight 的部分, 你可能需要大晚上爬起来运行测试);其二,这个测试部分的逻辑和真正的实现代码逻辑重复了。
public void testDisplayCurrentTime_whenever() {
// fixture setup
TimeDisplay sut = new TimeDisplay();
// exercise sut
String result = sut.getCurrentTimeAsHtmlFragment();
// verify outcome
Calendar
time = new DefaultTimeProvider().getTime();
StringBuffer expectedTime = new StringBuffer();
expectedTime.append("<span class=\"tinyBoldText\">");
if ((time.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) == 0)
&& (time.get(Calendar.MINUTE) <= 1)) {
expectedTime.append("Midnight");
} else if ((time.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) == 12)
&& (time.get(Calendar.MINUTE) == 0)) { // noon
expectedTime.append("Noon");
} else {
SimpleDateFormat fr = new SimpleDateFormat("h:mm a");
expectedTime.append(fr.format(time.getTime()));
}
expectedTime.append("</span>");
assertEquals(expectedTime, result);
}
- 加入 Test Stub 之后的测试
下面的Stub用来注入有效的间接输入,被称为Resnponder,是一个 Happy Path。如果是注入无效的间接输入,则会是Saboteur。
public void testDisplayCurrentTime_AtMidnight() throws Exception {
// Fixture setup:
// Test Double configuration
TimeProviderTestStub tpStub = new TimeProviderTestStub();
tpStub.setHours(0);
tpStub.setMinutes(0);
// Instantiate SUT:
TimeDisplay sut = new TimeDisplay();
// Test Double installation
sut.setTimeProvider(tpStub);
// exercise sut
String result = sut.getCurrentTimeAsHtmlFragment();
// verify outcome
String expectedTimeString = "<span class=\"tinyBoldText\">Midnight</span>";
assertEquals("Midnight", expectedTimeString, result);
}
- TimeProviderTestStub的具体实现
private Calendar myTime = new GregorianCalendar();
/**
* The complete constructor for the TimeProviderTestStub
* @param hours specify the hours using a 24 hour clock
* (e.g. 10 = 10 AM, 12 = noon, 22 = 10 PM, 0 = midnight)
* @param minutes specify the minutes after the hour
* (e.g. 0 = exactly on the hour, 1 = 1 min after the hour)
*/
public TimeProviderTestStub(int hours, int minutes) {
setTime(hours, minutes);
}
public void setTime(int hours, int minutes) {
setHours(hours);
setMinutes(minutes);
}
// Configuration Interface:
public void setHours(int hours) {
// 0 is midnight; 12 is noon
myTime.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, hours);
}
public void setMinutes(int minutes) {
myTime.set(Calendar.MINUTE, minutes);
}
// Interface used by SUT
public Calendar getTime() {
// @return The last time that was set:
return myTime;
}
2. Spy
Test Spy是指一个待测系统依赖组件的替身,并且会捕捉和保存待测对象对依赖系统的输出,这个输出会用于测试代码中的验证。 Test Spy主要用于记录和验证待测对象对依赖系统的输出。
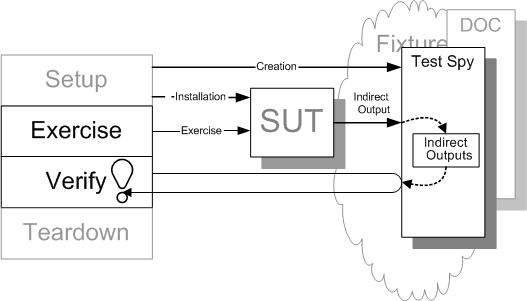
2.1 特点:
- 会将 Spy 内部的间接输出返回给测试用例,由测试用例进行验证
- 只负责获取内部信息,并把这些信息发出去,不负责验证信息的正确性
2.2 示例:
- 初始测试 下面的代码只是测试了基本的remove flight 的功能,不能验证SUT的间接输出,也就是每次 flight 被删除之后的请求日志, 包括数据、时间和用户。
public void testRemoveFlight() throws Exception {
// setup
FlightDto expectedFlightDto = createARegisteredFlight();
FlightManagementFacade facade = new FlightManagementFacadeImpl();
// exercise
facade.removeFlight(expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber());
// verify
assertFalse("flight should not exist after being removed", facade.flightExists( expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber()));
}
- 加入 Test Spy 之后的测试 下面的代码中,logSpy 就是 Test Spy,
facade.setAuditLog(logSpy)安装了 Test Spy,getDate,getActionCode等是Retrieval Interface(也称 Loopback)。
public void testRemoveFlightLogging_recordingTestStub() throws Exception {
// fixture setup
FlightDto expectedFlightDto = createAnUnregFlight();
FlightManagementFacade facade = new FlightManagementFacadeImpl();
// Test Double setup
AuditLogSpy logSpy = new AuditLogSpy();
facade.setAuditLog(logSpy);
// exercise
facade.removeFlight(expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber());
// verify
assertFalse("flight still exists after being removed", facade.flightExists( expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber()));
assertEquals("number of calls", 1, logSpy.getNumberOfCalls());
assertEquals("action code", Helper.REMOVE_FLIGHT_ACTION_CODE, logSpy.getActionCode());
assertEquals("date", helper.getTodaysDateWithoutTime(), logSpy.getDate());
assertEquals("user", Helper.TEST_USER_NAME, logSpy.getUser());
assertEquals("detail", expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber(), logSpy.getDetail());
}
- Spy 的具体实现
public class AuditLogSpy implements AuditLog {
// Fields into which we record actual usage info
private Date date;
private String user;
private String actionCode;
private Object detail;
private int numberOfCalls = 0;
// Recording implementation of real AuditLog interface:
public void logMessage(Date date, String user,
String actionCode,
Object detail) {
this.date = date;
this.user = user;
this.actionCode = actionCode;
this.detail = detail;
numberOfCalls++;
}
// Retrieval Interface:
public int getNumberOfCalls() {
return numberOfCalls;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
public String getActionCode() {
return actionCode;
}
public Object getDetail() {
return detail;
}
}
3. Mock
它类似于Test Spy,安插在待测系统内部,获取到待测系统内部的间接输出,一般根据调用者输入,按照约定执行操作, 然后返回调用者事先编码写好的预期结果。 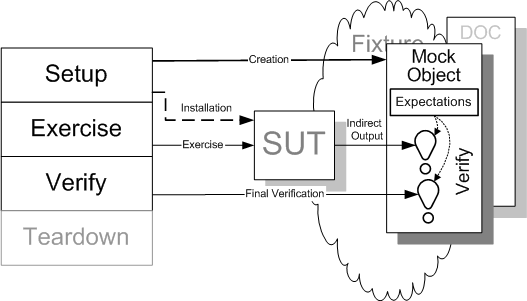
3.1 特点
- Mock还会对调用进行验证(verify),若碰到不在预期范围的调用还会抛出异常。
- Mock需要设置 expectation,而且必须要在 SUT的 exercise这一阶段之前进行设置。
Mock 的相应操作对应到Four Phrase如下:
- Fixture set up
- 构建 Mock Object
- 配置 Mock Object
- 安装 Mock Objct 到 SUT
- Exercise SUT
- SUT 调用 Mock Object,Mock Object 进行断言
- Result verification
- 测试调用最后的 verify 方法
- Fixture tear down
- 没有影响
3.2 示例
- 初始测试
public void testRemoveFlight() throws Exception {
// setup
FlightDto expectedFlightDto = createARegisteredFlight();
FlightManagementFacade facade = new FlightManagementFacadeImpl();
// exercise
facade.removeFlight(expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber());
// verify
assertFalse("flight should not exist after being removed", facade.flightExists( expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber()));
}
- 加入 Mock Object 之后的测试
public void testRemoveFlight_Mock() throws Exception {
// fixture setup
FlightDto expectedFlightDto = createAnonRegFlight();
// mock configuration
ConfigurableMockAuditLog mockLog = new ConfigurableMockAuditLog();
mockLog.setExpectedLogMessage( helper.getTodaysDateWithoutTime(),
Helper.TEST_USER_NAME,
Helper.REMOVE_FLIGHT_ACTION_CODE,
expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber());
mockLog.setExpectedNumberCalls(1);
// mock installation
FlightManagementFacade facade = new FlightManagementFacadeImpl();
facade.setAuditLog(mockLog);
// exercise
facade.removeFlight(expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber());
// verify
assertFalse("flight still exists after being removed",
facade.flightExists( expectedFlightDto.getFlightNumber()));
mockLog.verify();
}
4. Fake
Fake Object 和 Test Stub 很类似,都是依赖组件的代替,区别就在于Fake Object 更”轻量级”。”轻量级”是指Fake Object 仅仅提供和依赖组件一样的功能接口保证待测系统正常工作,让待测系统认为 Fake Object 就是”真的”依赖组件,实现细节可以非常简单, 不需要具有真实依赖组件的很多特性,也不需要像Test Stub那样接受测试的需求,返回特定response给待测系统。
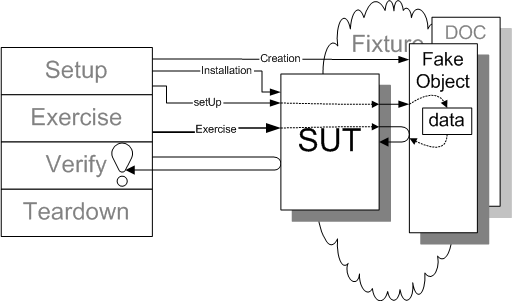
4.1 特点
- 轻量级、简单实现
- 不适合生产环境
4.2 场景
- 实际对象还未实现出来,先用一个简单的Fake Object代替它。
- 实际对象执行需要太长的时间
- 实际对象在实际环境下可能会有不稳定的情况。比如,网络发送数据包,不能保证每次都能成功发送。
- 实际对象在实际系统环境下不可用,或者很难让它变得可用。比如,使用一个依赖实际数据库的数据库访问层对象,必须安装数据库, 并且进行大量的配置,才能生效。
通常Fake Object用于构造下面的对象:
- Fake Database
- In-Memory Database
- Fake Web Service
- Fake Service Layer
4.3 示例
- 初始测试
public void testReadWrite() throws Exception{
// Setup:
FlightMngtFacade facade = new FlightMgmtFacadeImpl();
// Exercise:
BigDecimal yyc = facade.createAirport("YYC", "Calgary", "Calgary");
BigDecimal lax = facade.createAirport("LAX", "LAX Intl", "LA");
facade.createFlight(yyc, lax);
List flights = facade.getFlightsByOriginAirport(yyc);
// Verify:
assertEquals( "# of flights", 1, flights.size());
Flight flight = (Flight) flights.get(0);
assertEquals( "origin", yyc, flight.getOrigin().getCode());
}
- Service真实实现
public BigDecimal createAirport( String airportCode, String name,
String nearbyCity) throws FlightBookingException {
TransactionManager.beginTransaction();
Airport airport = dataAccess.createAirport(airportCode, name, nearbyCity);
logMessage("Wrong Action Code", airport.getCode());//bug
TransactionManager.commitTransaction();
return airport.getId();
}
public List getFlightsByOriginAirport( BigDecimal originAirportId) throws FlightBookingException {
if (originAirportId == null)
throw new InvalidArgumentException( "Origin Airport Id has not been provided",
"originAirportId", null);
Airport origin = dataAccess.getAirportByPrimaryKey(originAirportId);
List flights = dataAccess.getFlightsByOriginAirport(origin);
return flights;
}
public void setDao(Database dao) {
dataAccess = dao;
}
- 加入 Fake Object 之后的示例 下面的代码,将Fake Object InMemoryDatabase注入到了真实的 Service facade中,测试并没有更改太多,只是会调用 Fake 的 Database,整个测试执行会变快很多。
public void testReadWrite_inMemory() throws Exception{
// Setup:
FlightMgmtFacadeImpl facade = new FlightMgmtFacadeImpl();
facade.setDao(new InMemoryDatabase());
// Exercise:
BigDecimal yyc = facade.createAirport("YYC", "Calgary", "Calgary");
BigDecimal lax = facade.createAirport("LAX", "LAX Intl", "LA");
facade.createFlight(yyc, lax);
List flights = facade.getFlightsByOriginAirport(yyc);
// Verify:
assertEquals( "# of flights", 1, flights.size());
Flight flight = (Flight) flights.get(0);
assertEquals( "origin", yyc, flight.getOrigin().getCode());
}
- Fake Object 的实现
public class InMemoryDatabase implements FlightDao {
private List airports = new Vector();
public Airport createAirport(String airportCode, String name, String nearbyCity)
throws DataException, InvalidArgumentException {
assertParamtersAreValid( airportCode, name, nearbyCity);
assertAirportDoesntExist( airportCode);
Airport result = new Airport(getNextAirportId(), airportCode, name, createCity(nearbyCity));
airports.add(result);
return result;
}
public Airport getAirportByPrimaryKey(BigDecimal airportId)
throws DataException, InvalidArgumentException {
assertAirportNotNull(airportId);
Airport result = null;
Iterator i = airports.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Airport airport = (Airport) i.next();
if (airport.getId().equals(airportId)) {
return airport;
}
}
throw new DataException("Airport not found:"+airportId);
}
}
5. Dummy
Dummy Object对象是指为了调用被测试方法而传入的假参数,为什么说是假参数呢?实际上这些传入的Dummy对象并不会对测试有任何作用, 仅仅是为了成功调用被测试方法。所以,Dummy Object又被称为Dummy parameter或placeholder。
5.1 特点
- 测试中须传入的对象
- 测试中实际并不使用Dummy Object
5.2 场景
- Dummy Argument
- Dummy Attribute
5.3 示例
- 初始测试 下面的代码中,Invoice需要 Product 和 Customer 信息,但是 Customer的依赖信息为 Customer ->Address -> City -> State, 这就需要我们构造很多对象,让 Test setup 变得复杂起来。此外,测试只测试了 Invoice 相关的功能,并不关心 Address -> City -> State,因此冗余的代码会在某种程度上误导读者(该例子可能太简单,不足以说明)。
public void testInvoice_addLineItem_noECS() {
final int QUANTITY = 1;
Product product = new Product(getUniqueNumberAsString(), getUniqueNumber());
State state = new State("West Dakota", "WD");
City city = new City("Centreville", state);
Address address = new Address("123 Blake St.", city, "12345");
Customer customer= new Customer(getUniqueNumberAsString(), getUniqueNumberAsString(), address);
Invoice inv = new Invoice(customer);
// Exercise
inv.addItemQuantity(product, QUANTITY);
// Verify
List lineItems = inv.getLineItems();
assertEquals("number of items", lineItems.size(), 1);
LineItem actual = (LineItem)lineItems.get(0);
LineItem expItem = new LineItem(inv, product, QUANTITY);
assertLineItemsEqual("",expItem, actual);
}
- 加入 Dummy Object之后的测试 我们用 DummyCustomer 代替了实际的 Customer,而我们并不关系具体的实现,因为我们只是需要这个 Customer 对象作为一个参数输入。
public void testInvoice_addLineItem_DO() {
final int QUANTITY = 1;
Product product = new Product("Dummy Product Name", getUniqueNumber());
Invoice inv = new Invoice( new DummyCustomer() );
LineItem expItem = new LineItem(inv, product, QUANTITY);
// Exercise
inv.addItemQuantity(product, QUANTITY);
// Verify
List lineItems = inv.getLineItems();
assertEquals("number of items", lineItems.size(), 1);
LineItem actual = (LineItem)lineItems.get(0);
assertLineItemsEqual("", expItem, actual);
}
- Dummy Object 的实现
public class DummyCustomer implements ICustomer {
public DummyCustomer() {
// Real simple; nothing to initialize!
}
public int getZone() {
throw new RuntimeException("This should never be called!");
}
}
四、实现方式
- Hard-Coded Test Double - 会返回固定response的Test Double
- Configurable Test Double - 会根据测试需求返回相应response的Test Double
五、对比总结
| Pattern | Purpose | Has Behavior | Injects indirect inputs into SUT | Handles indirect outputs of SUT | Values provided by test(er) | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Double | Generic name for family | |||||
| Dummy Object | Attribute or Method Parameter | no | no, never called | no, never called | no | Null, “Ignored String”, new Object() |
| Test Stub | Verify indirect inputs of SUT | yes | yes | ignores them | inputs | |
| Test Spy | Verify indirect outputs of SUT | yes | optional | captures them for later verification | inputs (optional) | |
| Mock Object | Verify indirect outputs of SUT | yes | optional | verifies correctness against expectations | outputs & inputs (optional) | |
| Fake Object | Run (unrunnable) tests (faster) | yes | no | uses them | none | In-memory database emulator |
| Temporary Test Stub | Stand in for procedural code not yet written | yes | no | uses them | none | In-memory database emulator |
最后
有些开源框架中可能名字叫法不一样,比如 Junit 中使用Dummy Object代表本文中的Fake Object等。 因此,本篇文章主要是弄清楚一些形式,并不局限于概念的名称,理解才是关键。