一、Spring Batch流程
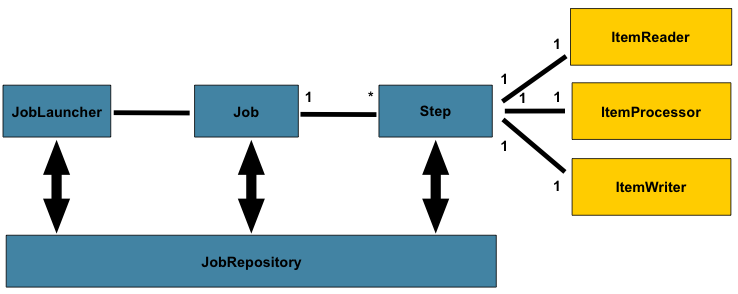 每个Batch都会包含一个Job,每个Job装了若干Step,Step读取数据,处理数据,然后将这些数据存储起来(ItemReader用来读取数据,ItemProcessor用来处理数据,ItemWriter用来写数据) 。JobLauncher用来启动Job,JobRepository是上述处理提供的一种持久化机制,它为JobLauncher,Job,和Step实例提供CRUD(Create\Retrieve\Update\Delete)操作。
每个Batch都会包含一个Job,每个Job装了若干Step,Step读取数据,处理数据,然后将这些数据存储起来(ItemReader用来读取数据,ItemProcessor用来处理数据,ItemWriter用来写数据) 。JobLauncher用来启动Job,JobRepository是上述处理提供的一种持久化机制,它为JobLauncher,Job,和Step实例提供CRUD(Create\Retrieve\Update\Delete)操作。
1 Job = Many Steps. 1 Step = 1 READ-PROCESS-WRITE or 1 Tasklet. Job = {Step 1 -> Step 2 -> Step 3} (Chained together)
从DB或是文件中取出数据的时候,read操作每次只读取一条记录,之后将读取的这条数据传递给processor(item)处理,框架将重复做这两步操作,直到读取记录的件数达到batch配置信息中”commin-interval”设定值的时候,就会调用一次write操作。然后再重复以上处理,直到处理完所有的数据。当这个Step的工作完成以后,或是跳到其他Step,或是结束处理。
二、Spring Batch Jobs
1、content.xml
content.xml中定义了批处理任务中需要的基础设施,主要配置任务仓库、任务调度器、任务执行中用到的事务管理器。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<!-- stored job-meta in memory -->
<bean id="jobRepository"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
</bean>
<!-- stored job-meta in database -->
<!--<bean id="jobRepository"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.JobRepositoryFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<property name="databaseType" value="mysql" />
</bean>-->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.batch.support.transaction.ResourcelessTransactionManager" />
<bean id="jobLauncher"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher">
<property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository" />
</bean>
</beans>
2、job-hello-world.xml
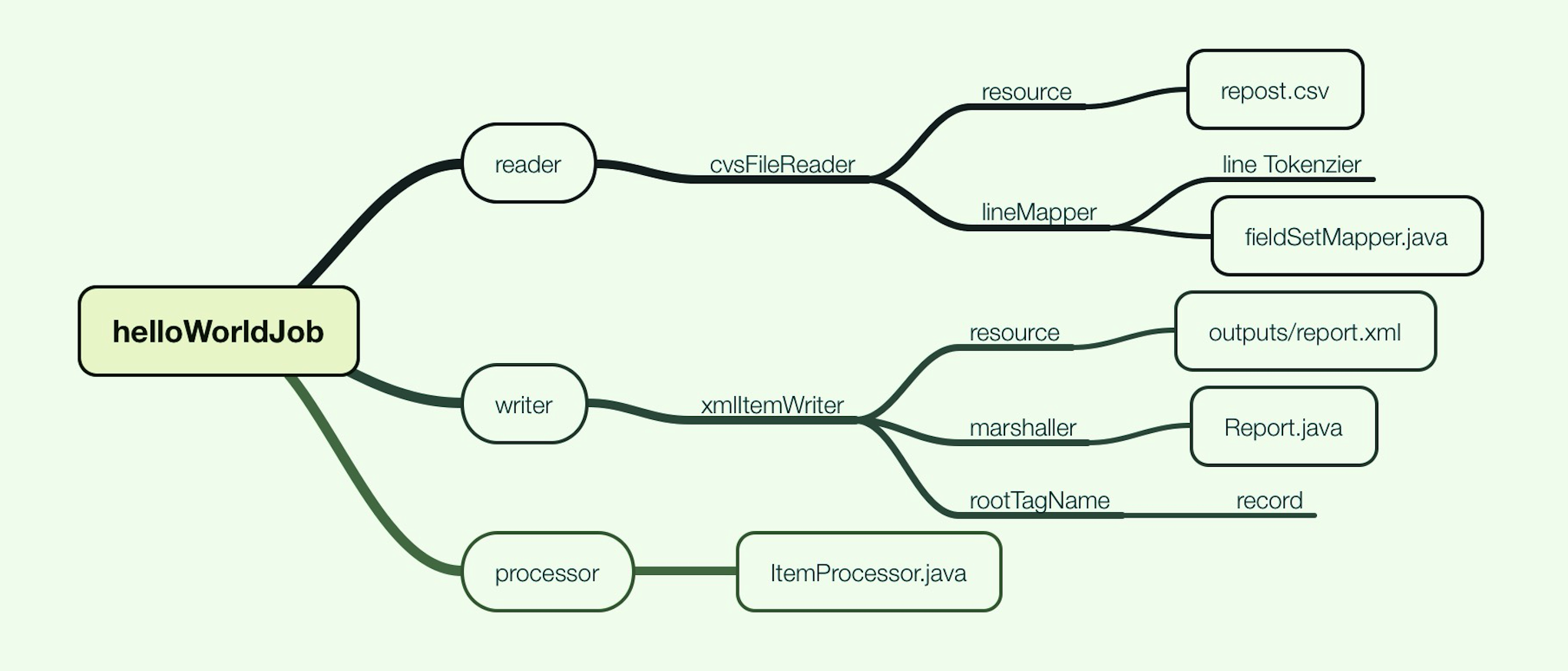 首先,helloWorldJob里面配置了读(cvsFileItemReader),写(xmlItemWriter) 以及处理(itemProcessor),并设置了commit-interval=”10”。
首先,helloWorldJob里面配置了读(cvsFileItemReader),写(xmlItemWriter) 以及处理(itemProcessor),并设置了commit-interval=”10”。
之后,对cvsFileItemReader中涉及的resource和lineMapper进行配置。对xmlItemWriter中涉及的resource、marshaller、rootTagName进行配置。而处理过程,则由稍后讲述的itemProcessor.java完成。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:batch="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch
http://www.springframework.org/schema/batch/spring-batch-2.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<import resource="../config/context.xml" />
<!--<import resource="../config/database.xml" />-->
<bean id="report" class="com.mkyong.model.Report" scope="prototype" />
<bean id="itemProcessor" class="com.mkyong.CustomItemProcessor" />
<batch:job id="helloWorldJob">
<batch:step id="step1">
<batch:tasklet>
<batch:chunk reader="cvsFileItemReader" writer="xmlItemWriter" processor="itemProcessor"commit-interval="10">
</batch:chunk>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<bean id="cvsFileItemReader" class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemReader">
<property name="resource" value="classpath:cvs/input/report.csv" />
<property name="lineMapper">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.DefaultLineMapper">
<property name="lineTokenizer">
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineTokenizer">
<property name="names" value="id,sales,qty,staffName,date" />
</bean>
</property>
<property name="fieldSetMapper">
<bean class="com.mkyong.ReportFieldSetMapper" />
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="xmlItemWriter" class="org.springframework.batch.item.xml.StaxEventItemWriter">
<property name="resource" value="file:xml/outputs/report.xml" />
<property name="marshaller" ref="reportMarshaller" />
<property name="rootTagName" value="report" />
</bean>
<bean id="reportMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller">
<property name="classesToBeBound">
<list>
<value>com.mkyong.model.Report</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
3、ReportFieldSetMapper.java
读取时,主要是通过ReportFieldSetMapper.java来完成report.csv到Report.java的映射。
package com.mkyong;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.FieldSetMapper;
import org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.FieldSet;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import com.mkyong.model.Report;
public class ReportFieldSetMapper implements FieldSetMapper<Report> {
private SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
@Override
public Report mapFieldSet(FieldSet fieldSet) throws BindException {
Report report = new Report();
report.setId(fieldSet.readInt(0));
report.setSales(fieldSet.readBigDecimal(1));
report.setQty(fieldSet.readInt(2));
report.setStaffName(fieldSet.readString(3));
//default format yyyy-MM-dd
//fieldSet.readDate(4);
String date = fieldSet.readString(4);
try {
report.setDate(dateFormat.parse(date));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return report;
}
}
4、report.csv
1001,"213,100",980,"mkyong", 29/7/2013
1002,"320,200",1080,"staff 1", 30/7/2013
1003,"342,197",1200,"staff 2", 31/7/2013
5、Report.java
package com.mkyong.model;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAttribute;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement(name = "record")
public class Report {
private int id;
private BigDecimal sales;
private int qty;
private String staffName;
private Date date;
@XmlAttribute(name = "id")
public int getId() {return id;}
public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}
@XmlElement(name = "sales")
public BigDecimal getSales() {return sales;}
public void setSales(BigDecimal sales) {this.sales = sales;}
@XmlElement(name = "qty")
public int getQty() {return qty;}
public void setQty(int qty) { this.qty = qty;}
@XmlElement(name = "staffName")
public String getStaffName() {return staffName;}
public void setStaffName(String staffName) {this.staffName = staffName;}
@XmlElement(name = "date")
public Date getDate() {return date;}
public void setDate(Date date) {this.date = date;}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Report [id=" + id +
", sales=" + sales +
", qty=" + qty +
", staffName=" + staffName +
"]";
}
}
6、CustomItemProcessor.java
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.batch.item.ItemProcessor;
import com.mkyong.model.Report;
public class CustomItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<Report, Report> {
@Override
public Report process(Report item) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Processing..." + item);
return item;
}
}
三、创建测试App
在App.java中
package com.mkyong;
import org.springframework.batch.core.Job;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobExecution;
import org.springframework.batch.core.JobParameters;
import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] springConfig = {"spring/batch/jobs/job-hello-world.xml"};
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(springConfig);
JobLauncher jobLauncher = (JobLauncher) context.getBean("jobLauncher");
Job job = (Job) context.getBean("helloWorldJob");
try {
JobExecution execution = jobLauncher.run(job, new JobParameters());
System.out.println("Exit Status : " + execution.getStatus());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Done");
}
}
四、结果
report.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<report>
<record id="1001">
<date>2013-07-29T00:00:00+08:00</date>
<qty>980</qty>
<sales>213100</sales>
<staffName>mkyong</staffName>
</record>
<record id="1002">
<date>2013-07-30T00:00:00+08:00</date>
<qty>1080</qty>
<sales>320200</sales>
<staffName>staff 1</staffName>
</record>
<record id="1003">
<date>2013-07-31T00:00:00+08:00</date>
<qty>1200</qty>
<sales>342197</sales>
<staffName>staff 2</staffName>
</record>
</report>
console:
Aug 26, 2015 8:15:40 PM org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher$1 run
INFO: Job: [FlowJob: [name=helloWorldJob]] launched with the following parameters: [{}]
Aug 26, 2015 8:15:40 PM org.springframework.batch.core.job.SimpleStepHandler handleStep
INFO: Executing step: [step1]
Processing...Report [id=1001, sales=213100, qty=980, staffName=mkyong]
Processing...Report [id=1002, sales=320200, qty=1080, staffName=staff 1]
Processing...Report [id=1003, sales=342197, qty=1200, staffName=staff 2]
Exit Status : COMPLETED
Aug 26, 2015 8:15:40 PM org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher$1 run
Done
INFO: Job: [FlowJob: [name=helloWorldJob]] completed with the following parameters: [{}] and the following status: [COMPLETED]
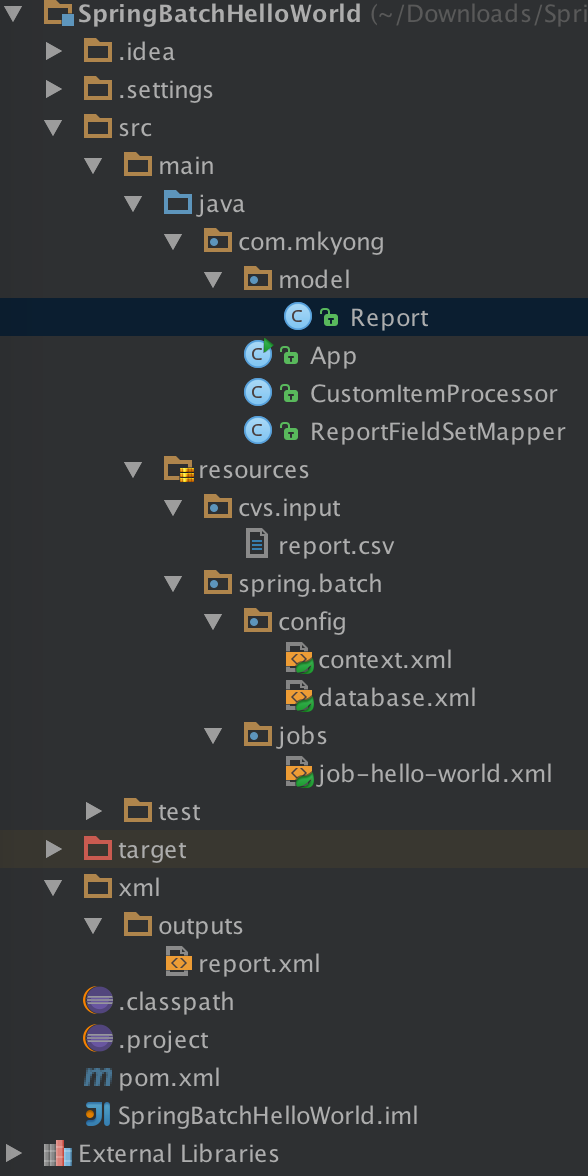
五、目录结构
六、主要领域对象
| 领域对象 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Job | Batch操作的基础单元 |
| Job Instance | 每次job执行时,都会生成一个实例,存放在JobRepository。 |
| Job Parameters | 不同的实例是通过job参数来区分的 |
| Job Execution | 负责具体Job的执行,每次运行Job都会启动一个新的Job执行器 |
| Job Respository | 负责存储Job执行过程中的状态数据及结果,为JobLaunter、Job、Step提供标准的CRUD实现。 |
| Job Launcher | 根据给定的Jon Parameter执行Job |
| Step | Job的一个执行环节,一个或多个step组装成Job,封装批处理任务中得一个独立连续阶段。 |
| Step Execution | 每次运行Step都会启动一个新的Step执行器 |
| Tasklet | Step中具体执行的逻辑操作,可以重复执行,可以设置具体的同步、异步操作等。 |
| Execution Context | 执行上下文,是一组框架持久化与控制的key/value对,能够让开发者在step Execution或Job Execution范畴保存需要进行持久化的状态。 |
| Item | 条目,一条数据记录 |
| Chunk | Item集合,它给定数量Item的集合,可以定义对Chunk的读操作、处理操作、写操作、提交间隔等。 |
| Item Reader | 条目读,其表示Step读数据,一次读取一条 |
| Item Processor | 条目处理,用于表示item的业务处理 |
| Item Writer | 条目写,用于表示Step输出数据,一次输出一批 |